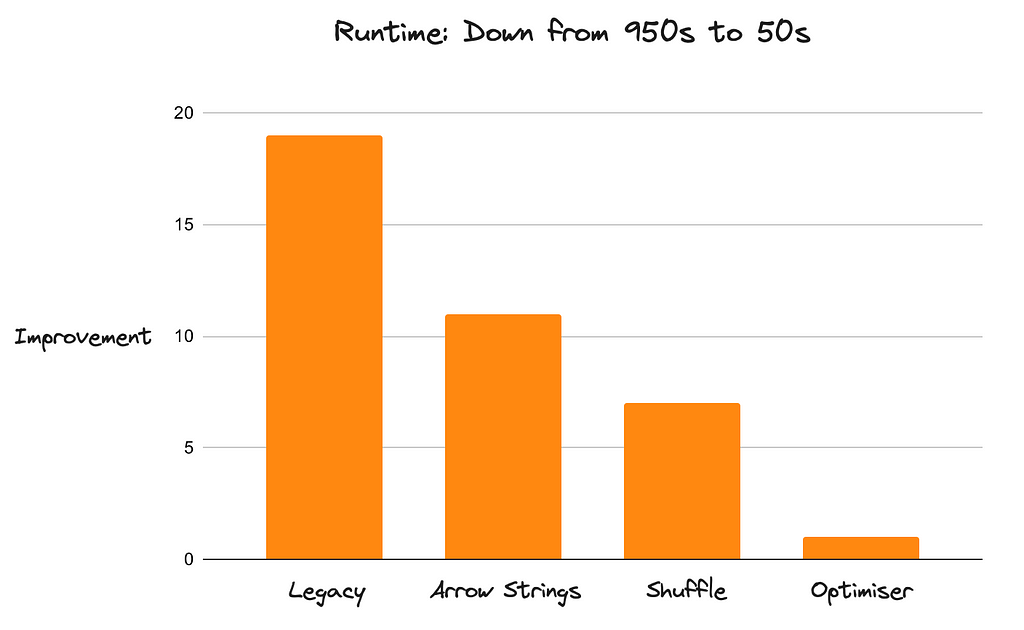
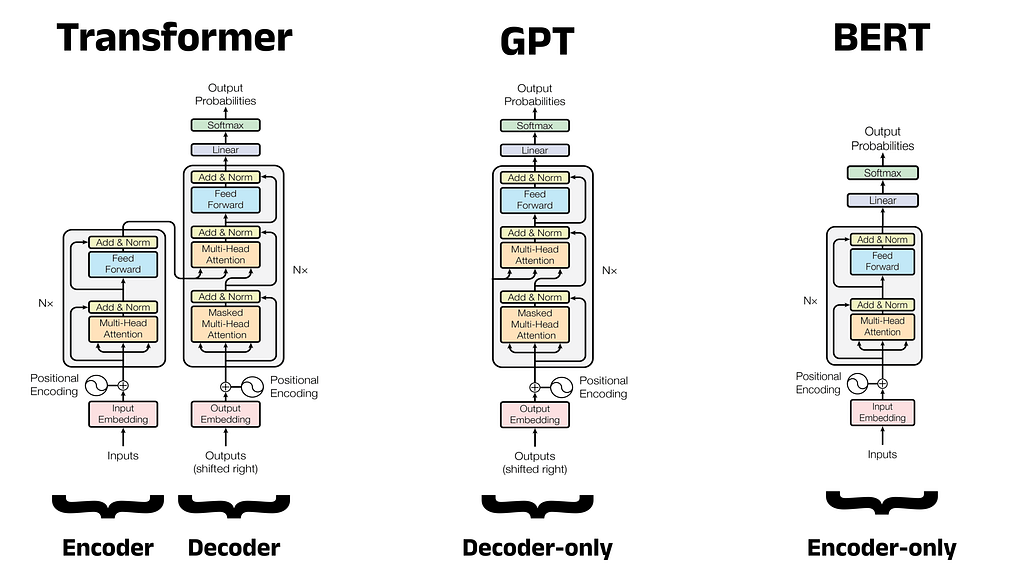
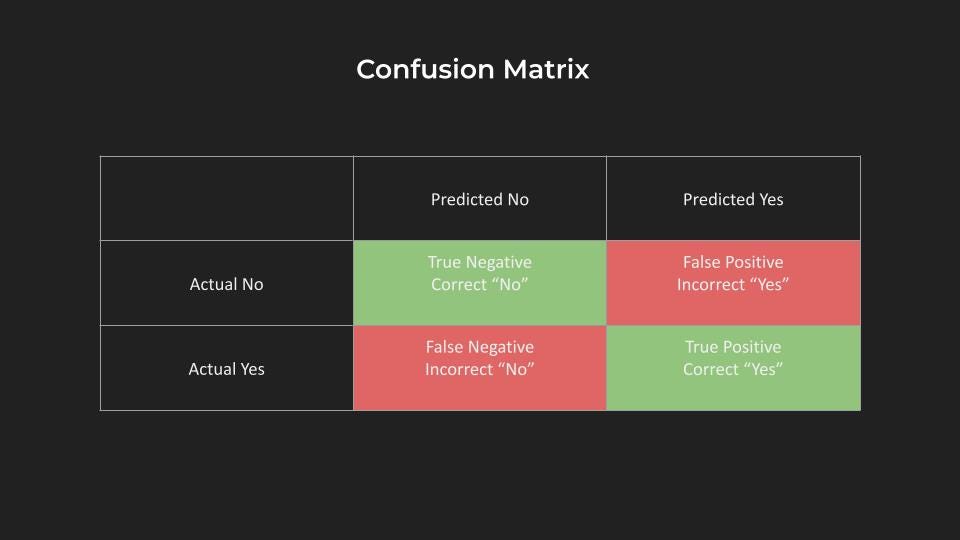
Friday, May 31, 2024
Thursday, May 30, 2024
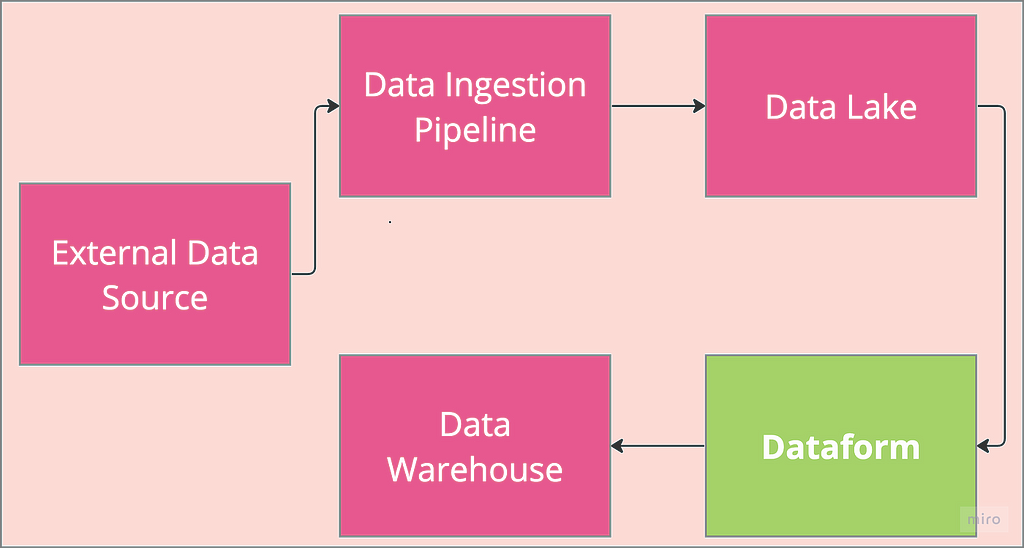
Terraforming Dataform
Tuesday, May 28, 2024
From Prompt Engineering to Agent Engineering
Data Scientists Work in the Cloud. Here’s How to Practice This as a Student (Part 2: Python)
Stepping out of the “comfort zone“ through domain adaptation — a deep-dive into dynamic prompting…
Monday, May 27, 2024
Embedding Markdown Files in a Streamlit Dashboard
Implement a Star Schema for Power BI Semantic Model: Step-by-Step Guide
AI-based organizational network analysis
Dask DataFrame is Fast Now
Sunday, May 26, 2024
Saturday, May 25, 2024
How to: Handle Missing Data for Time Series
Friday, May 24, 2024
Thursday, May 23, 2024
Two Common Pitfalls to Avoid When Doing Cross-Validation
Additive Decision Trees
Wednesday, May 22, 2024
Tuesday, May 21, 2024
In-Depth Support Vector Machines (SVMs) for Linear & Non-linear Classification & Regression
AI Knocking on the Classroom’s Door
Visualizing SQL Server Job History: Unlocking Hidden Capabilities with SQL Server Language…
Using LLMs to Learn From YouTube
Mastering Statistical Tests
Monday, May 20, 2024
Why does an Integer Need 28 Bytes in Python?
Unlock the Secrets to Skyrocket Vendor Central Profits: Eliminate Devastating Financial Scorecard Defects Now!
Unlock the Secrets to Skyrocket Vendor Central Profits: Eliminate Devastating Financial Scorecard Defects Now!

Unlock the Secrets to Skyrocket Vendor Central Profits: Eliminate Devastating Financial Scorecard Defects Now!
Tips, how-to’s, and best practices to optimize the health of your Vendor Central financials
Managing financial transactions within Amazon Vendor Central can be challenging, especially when dealing with late or short payments.
This guide provides a detailed overview of the Financial Scorecard, the common issues it highlights, and the corrective actions vendors can take to ensure smooth and timely payments.
Overview of the Financial Scorecard
The Financial Scorecard offers an in-depth analysis of transactions between vendors and Amazon over a specific period. It helps vendors understand the reasons behind late or short payments related to invoicing, catalog discrepancies, and supply chain issues.
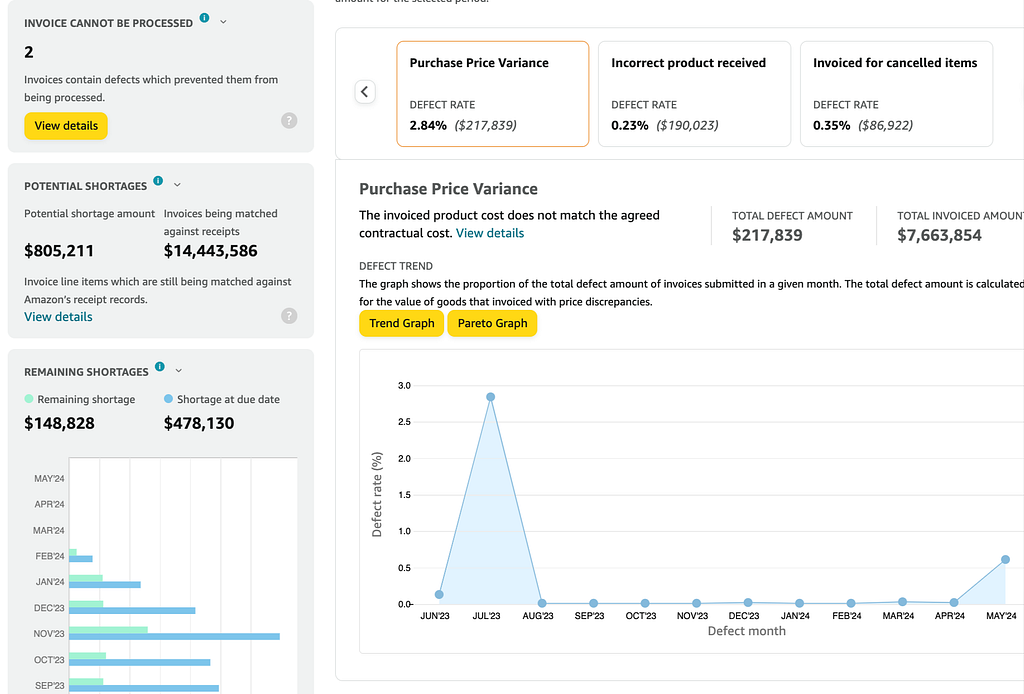
By using the Scorecard, vendors can identify potential gaps in their processes and receive guidance on addressing these issues to improve their business operations.
Common Issues and Corrective Actions
1. Missing Invoices
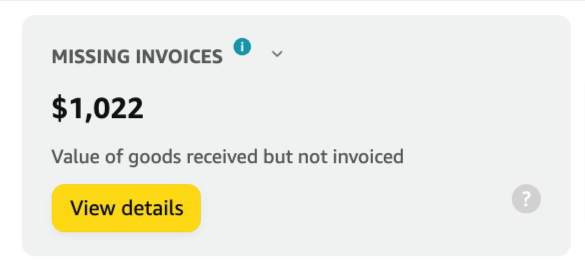
Issue Description:
- Instances where Amazon has received shipments but cannot locate the corresponding invoice.
Corrective Actions:
- Ensure an invoice is submitted when shipping products to facilitate timely payments.
- Avoid submitting invoices via paper or PDF, as these require manual processing and take longer to appear in the system.
- Ensure invoices comply with tax and compliance rules to prevent rejection.
- Do not submit duplicate invoices if one has already been sent.
2. Potential Shortages
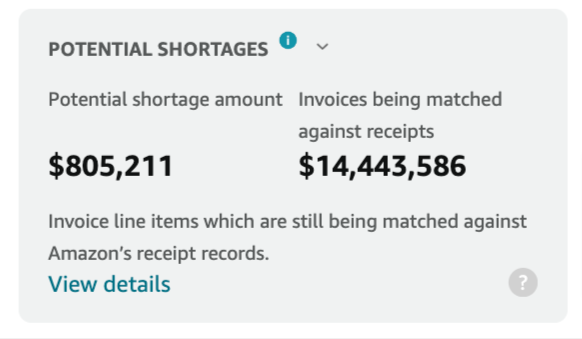
Issue Description:
- Invoice line items are still being matched against Amazon’s receipt records.
Corrective Actions:
- If products have not been shipped, send them promptly or submit a credit memo to release the invoice for payment.
- If the shipment has already been sent, wait for the ongoing matching activities to be completed.
- If items cannot be matched to receipts, they will be moved to remaining shortages.
3. Remaining Shortages
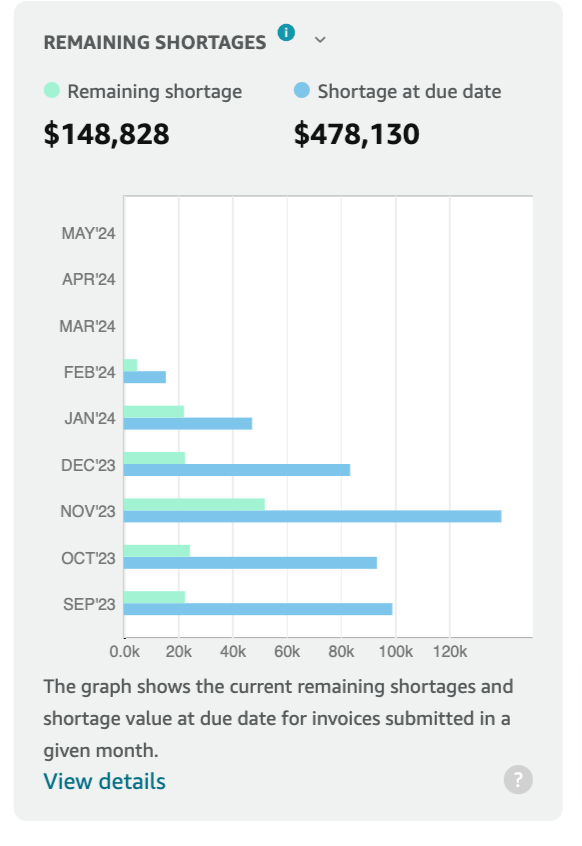
Issue Description:
- Shortages during the payment dispute process after invoice matching and reconciliation.
Corrective Actions:
- Resolve or cancel remaining shortages promptly.
- Send shipments for the shortage quantity within the delivery window to receive payments.
- Submit a credit memo for the shortage quantity if the shipment was not sent.
- Contact Amazon to cancel the Shortage Claim Reversal (SCR) invoice. An SCR invoice lists all remaining unpaid items on an invoice.
Detailed Defects Overview
The Defect Overview provides further insights into specific issues and their resolutions:
Product Not Listed on PO
Issue Description:
- The product on the invoice is not on the purchase order (PO).
Corrective Actions:
- Short-term Solution: Send a credit memo and a new invoice with the correct items.
- Long-term Solution: Ensure invoiced products match the ordered ones and contact Amazon for catalog mapping verification if necessary.
Invoiced Quantity Greater Than Ordered Quantity
Issue Description:
- The invoiced quantity exceeds the quantity on the PO.
Corrective Actions:
- Short-term Solution: Submit a credit memo for the excess quantity.
- Long-term Solution: Ensure the invoice reflects the exact quantity ordered.
Unrecognized Product
Issue Description:
- The product ID on the invoice is not recognized in Amazon’s catalog.
Corrective Actions:
- Short-term Solution: Correct ID issues in the catalog and resubmit the invoice.
- Long-term Solution: Ensure the invoiced and shipped product ID matches the product ordered.
Multiple ASINs for a Single Product
Issue Description:
- The product ID on the invoice refers to multiple ASINs.
Corrective Actions:
- Short-term Solution: Verify and correct the product ID.
- Long-term Solution: Update product details regularly through Items > Edit Products.
Incorrect Unit vs Pack Quantity
Issue Description:
- The product quantity and cost specified on the invoice do not match the PO.
Corrective Actions:
- Short-term Solution: Verify consistency between the PO and the invoice.
- Long-term Solution: Regularly update product details to ensure accuracy.
Late Shipping
Issue Description:
- The shipment arrived at least 14 days after the product was invoiced or the invoice was due for payment.
Corrective Actions:
- Short-term Solution: Ensure timely delivery by coordinating with your carrier.
- Long-term Solution: Issue the invoice on the same day as dispatch and deliver within the PO delivery window.
Invoiced for Cancelled Items
Issue Description:
- Supplying products for purchase order items that were canceled before invoice submission.
Corrective Actions:
- Short-term Solution: Check internal data to verify the items sent and send a credit memo for incorrect items.
- Long-term Solution: Ensure timely delivery and avoid invoicing canceled items.
Incorrect Product Received
Issue Description:
- The received products differ from the invoiced products.
Corrective Actions:
- Short-term Solution: Send a credit memo for the wrong items and a new invoice with the correct items.
- Long-term Solution: Ensure the warehouse team ships products listed on the invoice and PO.
Deleted Appointment
Issue Description:
- The truck delivering the shipment failed to arrive or was rejected at the fulfillment center.
Corrective Actions:
- Short-term Solution: Ensure the carrier arrives at the correct delivery slot.
- Long-term Solution: Create valid appointments for truck deliveries and respect delivery dates.
Purchase Price Variance
Issue Description:
- The invoiced product cost does not match the agreed contractual cost.
Corrective Actions:
- Short-term Solution: Ensure no variance between the PO price and invoice price.
- Long-term Solution: Update product costs as soon as changes occur.
Liquidated Products
Issue Description:
- Delivered products not listed in Amazon’s catalog could not be received.
Corrective Actions:
- Short-term Solution: Send a credit memo for the wrong items.
- Long-term Solution: Ensure the warehouse team ships the products listed on the invoice and PO.
Overages Not Invoiced
Issue Description:
- Items shipped but not ordered or invoiced.
Corrective Actions:
- Short-term Solution: Verify the shipped quantity and submit an invoice for the correct quantity.
- Long-term Solution: Ensure the warehouse team ships the quantity of units confirmed in the PO.
Invoice Cannot Be Processed
Issue Description:
- Invoices containing defects preventing processing.
Corrective Actions:
- Short-term Solution: Check rejected invoices and correct the issues.
- Long-term Solution: Follow the correct guidelines to create and submit invoices.
Submitting a Credit Note (Memo)
When managing your financial transactions with Amazon Vendor Central, you may occasionally need to submit a credit note (memo) if an invoice is placed on hold due to a quantity shortage or price discrepancy. Submitting a credit note helps resolve these issues promptly and ensures your payment process continues smoothly.
Steps to Submit a Credit Note:
Navigate to Payments > Invoices:
- This section allows you to manage and review all your invoices.
Review/Dispute Shortages:
- In the Available Actions section, click on “Review/Dispute shortages”.
- This will allow you to select the specific invoice that requires a credit note.
Select an Action on the Invoice:
- Select the invoice in question and click on “Actions.”
View Invoice Details and Submit Credit Memo:
- In the Available Actions window, click on “View Invoice details”.
- Then, click on “Submit credit memo.”
- Note: You can create a credit note for the total amount or a partial credit note by clicking “Submit ASIN level details.”
Enter Required Details and Submit:
- Fill in the necessary details for the credit note.
- Once all details are entered correctly, click “Submit”.
Alternative Method via Financial Dashboard:
- You can also submit a credit note from the Financial Dashboard:
- Click on “In progress” under “Your payables.”
- Select the invoice that needs a credit memo.
- Choose “Submit credit memo” from the Available Actions drop-down menu.
Following these steps, you can efficiently manage discrepancies and ensure your invoices are processed without delays. Submitting credit notes promptly helps maintain a healthy cash flow and keeps your transactions with Amazon running smoothly.
Understanding Provisions for Receivables
Provisions for receivables are essential to managing your financial transactions with Amazon, mainly when dealing with returns, marketing expenses, and rebates. These provisions act as temporary credit memos, ensuring your account remains balanced even when forecasted costs exceed forecasted payments.
What are Provisions for Receivables?
Provisions for receivables are temporary credit memos that Amazon can place on your account. They are used when the forecasted costs associated with returns, marketing, and rebates due to Amazon exceed the forecasted payments owed to you. The primary purpose of these provisions is to prevent these costs from creating a debit balance on your account.
How Provisions Work:
- Deduction from Payments: Provisions are deducted from the payments due to you.
- Subsequent Adjustment: These provisions are subject to subsequent adjustments based on the actual costs of returns, marketing, and rebates, as well as the actual payments due to you.
Provision Placement:
- When a provision is placed on your account, it will be dated and displayed in the format YYMMDD_PROVISION_FOR_RECEIVABLES.
- For example, a date of 161017 on your remittance means that the provision was placed on October 17, 2023.
Reversing Provisions for Receivables
Temporary Nature:
- The provision for receivables will reverse when invoices for returns, marketing, and rebates are settled or when a decision is made not to return the inventory.
- When a provision is reversed, it will display as YYMMDD_PROVISION_FOR_RECEIVABLESR.
Daily Recalculation:
- Provisions are recalculated, adopted, or reversed daily.
- No invoice copies are associated with these provisions since they are not “real” deductions.
Understanding and managing provisions for receivables helps ensure that your account remains balanced and that you can accurately forecast your financial position with Amazon.
By keeping track of these temporary credit memos and their adjustments, you can maintain a clearer picture of your overall financial health and prevent any unexpected debit balances on your account.
Improving Your Financial Transactions
Vendors can significantly improve their financial transactions with Amazon by regularly reviewing the Financial Scorecard and addressing the issues it highlights.
Here are some general tips for maintaining smooth operations:
- Consistency: Always ensure that invoiced quantities and costs match those on the PO.
- Accuracy: Double-check all details before submitting invoices to avoid rejections and delays.
- Communication: Maintain open communication with Amazon to resolve any discrepancies promptly.
For further training and support, vendors can access additional resources through Vendor Central > Support > Training topics.
By understanding and utilizing the Financial Scorecard, vendors can minimize payment issues, streamline their invoicing processes, and enhance their overall business performance with Amazon.
Unlock Effortless Financial Insights With Our Code-Free Vendor Central Integration
Are you struggling with complex, messy financial data management for Vendor Central? Say goodbye to the hassle.
The Amazon Selling Partner API (SP-API) allows for direct, automated access to Amazon forecasting data, making it easier for businesses to integrate it into their systems. Openbridge allows Amazon Vendors to save time manually downloading reports, increasing data velocity and reducing errors in messy merging and tracking downloaded reports.
Openbridge automation extends beyond financial data to a broad collection of Amazon and non-Amazon data sources;
- Brand Analytics
- Retail Analytics
- Retail Procurement
- Direct Fulfillment
- Real-time Traffic, Sales, and Inventory
- Amazon Advertising
Openbridge offers a seamless, automated solution that unifies your data into a private, trusted data warehouse or data lake like Amazon Redshift, Databricks, Google BigQuery, and more — all without a single line of code. With your data unified, you can use your favorite analytic tools like Power BI, Looker, Tableau, and others for internal teams or external partners.
Automate And Unify Your Vendor Central Data — Free For 30 Days
Start your journey towards data-driven growth and profit with Openbridge. Our code-free, fully automated Selling Partner API integration simplifies your Amazon Vendor Central operations.
Ready to harness the power of your Vendor data?
→ Sign Up Now for Your Free 30-day Trial For Amazon Vendor Central Data Automation.
Unlock the Secrets to Skyrocket Vendor Central Profits: Eliminate Devastating Financial Scorecard Defects Now! was originally published in Openbridge on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
from Openbridge - Medium https://ift.tt/NMFJPnO
via Openbridge
A Guide to Powerful Python Enumerations
Sunday, May 19, 2024
A Complete Guide to BERT with Code
Saturday, May 18, 2024
Decoding Time: Unraveling the Power of LSTM vs. N-BEATS for Accurate Time Series Forecasting
Are GPTs Good Embedding Models
Please Make this AI Less Accurate
Friday, May 17, 2024
Common Causes of Data Leakage and how to Spot Them
Amazon Vendor Central Purchase Orders: The Missing Guide

Explore How The Vendor Central Purchase Order Fulfillment Lifecycle Operates
Whether you’re a seasoned operator in Amazon Vendor Central or just trying to understand what a vendor journey on Amazon involves, this guide will be a reference point for daily operations, avoiding potential pitfalls, and maximizing the potential of a partnership in Amazon Vendor Central.
7 Steps In The Amazon Vendor Central Purchase Order Fulfillment Lifecycle
If you are a Vendor, you are well aware there are seven critical stages of the Purchase Order Fulfillment Lifecycle:
- PO Submission
- PO Confirmation
- Transportation Management
- Pick, Prep, and Pack
- Label and Build Pallet
- Submit Shipment
- Shipment Received
Each step highlights Amazon’s order processing and inventory decisions in Amazon Vendor Central.
1. PO Submission
The lifecycle begins with the submission of an Amazon purchase order.
- Automatic Orders: Generated and submitted automatically based on a schedule for each vendor code.
- Manual Orders: Created manually by an In-Stock Manager for specific, non-regular needs.
This initial step involves selecting and finalizing the products ordered from the supplier in Amazon Vendor Central.
2. PO Confirmation
Review and confirm the products. Vendors must confirm PO actions within 48 hours of receipt.
- Product Availability: Confirm if the products can be shipped within the requested window.
- Shipping Capability: Provide information on when the products can be shipped or delivered.
- Quantity Details: Specify how many units of each product can be shipped.
Vendors in Amazon Vendor Central must accept or reject orders promptly to ensure smooth processing.
3. Transportation Management
Secure your shipment pick-up or delivery date. Transportation management in Amazon Vendor Central involves coordinating with carriers and scheduling shipments effectively.
Types of Vendors:
- Collect (WePay) Vendors: Pay a Freight Allowance and use Amazon-provided carriers.
- Prepaid (TheyPay) Vendors: Manage their shipping and use their carriers.
Vendors should submit routing requests on the order day to secure optimal shipping routes and times.
4. Pick, Prep, and Pack
Prepare the ordered products for shipment. Ensure compliance with Amazon Vendor Central packaging standards to maintain product integrity during transit.
- Packaging Standards: Products must be ready to ship before storage, adhering to specific packaging standards.
- Resources: Visit the Support > View Resource Center for packaging requirements and search for “Amazon Packaging Certification” for better packaging practices.
5. Label and Build Pallet
Organize and label shipments.
- Label & Build: Each pallet is labeled with relevant shipping and order information. This labeling is essential for tracking and ensuring the correct items are shipped and received in Amazon Vendor Central.
6. Submit Shipment
Notify the buyer of shipment details. Ensures proper planning and reception of the shipment, providing insight into the contents and expected arrival.
- Advance Shipment Notification (ASN): The ASN is a crucial document that provides detailed information about the shipment. Must be sent within 30 minutes of the carrier’s departure or 6 hours before arrival at the fulfillment center, whichever is earliest.
7. Shipment is Received
Completion of the fulfillment process.
- Breakdown of Pallets to Cartons: Upon arrival at the fulfillment center, the shipment is broken down from pallets into individual cartons or packages for easier handling and sorting.
- Scanning and Verification: Each carton label is scanned using a Parcel Identifier (PID) scanner to match the data submitted in the ASN.
- Unpacking Cartons: Cartons are unpacked, and products are placed into totes for sorting according to their final delivery destinations.
- Storing Products on Shelves: Unpacked and sorted products are stored on shelves in the fulfillment center and ready to be shipped to customers.
The final step in Amazon Vendor Central ensures that the received products are processed and prepared for final delivery to the customer.
Causes of Amazon Purchase Order Modifications
Amazon may modify a PO as they are not set in stone. The following are a few causes for a PO to be modified
1. Cancellation:
- Vendor Non-Acceptance: POs may be canceled if they do not accept unconfirmed POs before they are automatically canceled.
- Non-Receipt of Confirmed Quantities: If the accepted quantity on confirmed POs isn’t received by the expected-to-receive timelines, the POs are automatically canceled.
- Issuance Errors: POs that are issued in error by Amazon will be canceled.
2. Accepted Quantity Updated:
- Increase Requests: If a vendor’s request to increase the accepted quantity on confirmed POs is approved by Amazon, the accepted quantity will be adjusted accordingly.
3. Ship/Delivery Window Updated:
- Extension Requests: If a vendor’s request for an extension of the shipping or delivery window is approved by Amazon, the timeline will be modified to match the new requested window.
4. Ship-to Location Updated:
- Capacity Issues: If the initial ship-to-location encounters capacity issues, it may be modified to prevent delays in receiving the vendor’s shipments.
5. PO Item Cost Updated:
- Cost Change Requests: If a vendor’s request for a change in the cost price of a PO item is approved by Amazon, the item cost will be updated to reflect the new amount.
Modification History Accessibility
- Start Date: The modification history is accessible from September 8, 2023.
- Duration: History records go back up to six months.
- Viewing Instructions: To review past modifications within the specified timeframe, deactivate the “Hide viewed items” toggle next to the search bar.
Communicating Product Availability in Amazon Vendor Central
Effective communication of product availability is crucial for optimizing the purchase order fulfillment process and ensuring accuracy throughout the supply chain in Amazon Vendor Central.
Methods to Communicate Product Availability
1. Before a Purchase Order is Placed:
- How to Communicate: Navigate to Items > Catalog. Utilize the Update Availability feature to verify and update product availability instantly.
2. After a Purchase Order is Placed:
- Current Purchase Orders: Go to Orders > Purchase Orders. Use Purchase Order Acknowledgement Statuses to accept or reject orders. (See the Amazon Selling Partner API for more details)
- Future Purchase Orders: Use the Update Availability feature to communicate changes in product availability.
Importance of Communication
- Impact on Amazon’s Decisions: The availability signals sent by vendors influence Amazon’s purchasing strategies and the management of catalog availability, thereby affecting future buying decisions and the acknowledgment of purchase orders.
Interpretation of Availability Signals
- In Stock: Accepted (AC): Indicates products are in stock and expected to be fulfilled within PO policy terms.
- Backordered: Variants include not yet available (BA), not yet published (BX), or to be reprinted (BR).
- Temporarily Unavailable: This includes various cancellation statuses, such as out of stock (OS) or temporarily out of stock (IR). Soft rejection may occur, leading to potential suspension of orders if repeated.
- Permanently Unavailable: Statuses like permanently out of stock (CK), out of print (OP), or obsolete (CP) lead to a hard rejection, potentially resulting in indefinite suspension of orders for that product.
Actions and Consequences
- Acceptance: Expectation to fulfill the product as per the terms specified.
- Soft Reject: The product might be ordered again in the future. Frequent soft rejections can lead to a 30-day suspension of orders for the products.
- Hard Reject: Indicates that the product will not be available. Repeated hard rejections may cause an indefinite suspension of orders for the product.
No Purchase Orders in Amazon Vendor Central
Occasionally, vendors may encounter situations where no purchase orders are available in Amazon Vendor Central. This section outlines potential reasons and steps to address the issue.
Possible Reasons for No Purchase Orders
- Product Availability Issues: If product availability signals indicate frequent out-of-stock statuses or backorders, Amazon may suspend placing new purchase orders for those items.
- Performance Metrics: Poor performance metrics, such as low on-time delivery rates or high defect rates, can lead to a reduction or cessation of purchase orders.
- Changes in Demand: Shifts in consumer demand or changes in Amazon’s purchasing strategy may result in fewer or no purchase orders for specific products.
Steps to Address the Issue
- Review Availability Signals: Ensure product availability signals are accurate and up-to-date in Amazon Vendor Central.
- Improve Performance Metrics: Improve key performance metrics such as on-time delivery rates and reducing defect rates.
- Communicate with Amazon: Contact Amazon Vendor Central support to understand the reasons for the lack of purchase orders and seek guidance on corrective actions. By understanding the potential reasons and taking proactive steps, vendors can address the issue of no purchase orders in Amazon Vendor Central and work towards restoring regular order placements.
Automate And Unify Your Vendor Central Purchase Order Data— Free For 30 Days
Our direct, code-free data integration for Amazon Vendor Central Retail Procurement provides reliable, integrated data automation solutions that allow you to;
- Unify data in a trusted, private industry-leading data lake, data lakehouse, or cloud warehouses like Databricks, Amazon Redshift, Amazon Redshift Spectrum, Google BigQuery, Snowflake, Azure Data Lake, Ahana, and Amazon Athena. Data is always wholly owned by you.
- Take control, and put your data to work with your favorite analytics tools. Explore, analyze, and visualize data to deliver faster innovation while avoiding vendor lock-in using tools like Google Data Studio, Tableau, Microsoft Power BI, Looker, Amazon QuickSight, SAP, Alteryx, dbt, Azure Data Factory, Qlik Sense, and many others.
Get a 30-day free trial of the Openbridge Amazon Vendor Central Retail Procurement.
Amazon Vendor Central Purchase Orders: The Missing Guide was originally published in Openbridge on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
from Openbridge - Medium https://ift.tt/UZTjSFW
via Openbridge